How to Get Rid of Mycoplasma in Cell Culture
Introduction
Mycoplasma contamination of cultured cells poses a serious challenge to biological and biopharmaceutical studies, since infection rates of cell cultures can range from 15 to 100% (Kazemiha et al., 2016). Although a number of methods have been evaluated to eliminate Mycoplasma contamination, treatment of cell cultures with antibiotics remains the most widely used because it is simple and rapid (Drexler and Uphoff, 2002; Hopfe et al., 2013). However, using antibiotics to eliminate Mycoplasma contamination has some serious limitations. Some bacteriostatic antimicrobial agents inhibit Mycoplasma growth without completely eradicating the contaminant (Lincoln and Gabridge, 1998), while some anti-Mycoplasma antibiotics have no effect because of the development of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma (Drexler and Uphoff, 2002). Additionally, although some antibiotics, such as aminoglycosides and lincosamides are effective at eradicating Mycoplasma contamination, they are cytotoxic to the cultured cells (Drexler and Uphoff, 2002; Laleh Nikfarjam, 2012). Recent data also suggested that some anti-Mycoplasma antibiotics are mostly effective in the extracellular media and not as much against intracellular Mycoplasma (Degeling et al., 2012).
Alternative ways to effectively eliminate Mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures include co-cultivating contaminated cells with primary human or mouse macrophages in vitro or by passaging contaminated cells in mice (Schimmelpfeng et al., 1980; Howell et al., 1982; Lombardo and Lanks, 1982; Roseto et al., 1984; Carroll and O'Kennedy, 1988; Hirschberg et al., 1989). In addition to the fact that acquisition of human macrophages is an expensive and demanding procedure, techniques for co-culture of contaminated cells with human or mice macrophages in vitro are not well-standardized. In vivo strategies whereby BALB/c mice are intraperitoneally injected with contaminated cells may therefore be the most effective mean of eliminating Mycoplasma contamination.
The major concerns and challenges of in vivo passage of cells in mice include (1) long duration (20–54 days) of in vivo passage (Lombardo and Lanks, 1982); (2) the possibility of cross-contamination of mouse and human cells (Schimmelpfeng et al., 1980); (3) changes in cell function (e.g., proliferation, gene expression and protein expression) after in vivo treatment; (4) the possibility of changes in cell characteristics such as short tandem repeats (STR), (5) the possibility that intracellular Mycoplasma cannot be cleared by in vivo treatment; and (6) the risk of infection with xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV) (Naseer et al., 2015).
In this study, we evaluated a method to eliminate Mycoplasma hyorhinis (M. hyorhinis) contamination from C3A human hepatocytes without antibiotic treatment. Our technique included injection of normal BALB/c mice with paraffin oil prior to injection with cells in order to shorten the duration of in vivo passage. We validated the effectiveness of this strategy by continuous PCR, Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Hoechst 33258 staining.
Materials and Methods
Cell Cultures
Mycoplasma-free human hepatocyte C3A cells, a clonal derivative of Hep G2 cells with high albumin (ALB) production, were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Before the in vivo experiment, continuous PCR and DNA sequencing confirmed that C3A used in this study had been contaminated by Mycoplasma for more than 1 month. Cells were grown to adherence in standard plastic plates and flasks (Biofil, Guangzhou, China) in Eagle's minimum essential medium (EMEM) (ATCC Lot:63609149) supplemented with 20% Mycoplasma-free, heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, Lot:42F5364K). Cultures were maintained at 37°C, in the presence of 5% CO2 and 90% humidity. No other supplements (such as antibiotics) besides FBS were added to the culture medium. Mycoplasma-infected and uninfected cells were cultured in separate incubators in order to avoid cross-contamination. Cells were thawed and cultured for 6 days before being used for elimination experiments. The cured cells which were harvested at Day 49 were designated as Tc. Non-treated contaminated cells cultured for 6 days after being thawed were designated as 1d M(+) cells, and non-infected cells were designated as M(−) cells. 1d M(+) cells which were further cultured in vitro for 43 days were designated as 43d M(+) cells.
Mycoplasma Detection and Identification
Cell culture supernatants were collected every 7 days from the different experimental groups and stored in sterile DNA-free microcentrifuge tubes at −20°C. Mycoplasma contamination was detected by PCR using primers specifically designed toward a highly conserved 16S rRNA coding region of the Mycoplasma genome that can be used to identify the most common infecting species (Huada, Shenzhen, China) Primer sequences are listed in Table 1. Cell culture supernatants were thawed on ice and directly used for PCR. The PCR reaction mixture contained 5 μL of culture supernatant, 0.5 μL each of forward and reverse primers, 10 μL of 2 × PCR Master mix (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan, Cat: KOD 401) and 4 μL deionized water (ddH2O). The positive control reaction contained 2 μL of DNA sample from the M. hyorhinis genome (>104 copies, Primerdesign, England), and the negative control contained 2 μL of deionized water instead of the sample. Cycling conditions included an initial denaturation step for 5 min at 95°C, followed by 35 cycles of 94°C for 1 min, 57°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 1 min. The final elongation was done at 72°C for 6 min. PCR reaction products (5 μL) were analyzed on 1.4% agarose gels. Mycoplasma species were identified by subjecting PCR reaction products to bidirectional sequencing by The Beijing Genomics Institute (Shenzhen, China). All DNA sequence data were blast-searched against the NCBI Nucleotide database.

Table 1. Primers for PCR and qRT-PCR.
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Tc, 1d M(+) cell, and 43d M(+) cell were collected for TEM analysis and to confirm the PCR results. Cells were fixed for 12 h in a solution of 2% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M PBS, and then exposed to a solution of 2% osmium tetraoxide in 0.1 M PBS for 1 h. The samples were dehydrated in ethanol, infiltrated with a mixture of ethanol and epoxy resin (1:1) for 1 h and polymerized with pure epoxy resin at 60°C for 18 h. Ultra-thin sections (90 nm), were mounted on 200-mesh thin-bar copper grids (Agar) and stained with uranyl acetate and Reynold's stain. Sections were subjected to TEM (H-7500, Hitchi, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 60 Kv.
Determination of Colony-Forming Units (CFU) of Mycoplasma of Cell Suspensions
Contaminated cell cultures were centrifuged and the pellets were resuspended with PBS. Suspensions of Mycoplasma-contaminated cells (4 × 106 cells/ml) were serially diluted and 0.1 ml of each dilution was inoculated on Mycoplasma agar base (Senbeijia, SBJ-ME-1274, China) supplemented with 10% horse serum (Gibco, 26050070, New Zealand) and 100 U/ml penicillin. The agar plates were then incubated at 37°C for 7 days. Colonies on agar plates were stained with Dienes (Senbeijia, SBJ-1744, China) for Mycoplasma counting.
Animals
Adult female BALB/c mice (8–10 weeks old) were purchased from the Southern Medical University Animal Laboratories. Mice were fed standard forage and housed in cages within sound-attenuated, temperature-controlled isolation chambers with a 12:12 light-dark cycle (lights on at 4 a.m.) at 22°C ambient temperature. To avoid any chance of cross-contamination of Mycoplasma between mice, mice were individually housed in cages. All animal work was conducted in compliance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. All animal protocols were approved by Animal Ethics Committee of the Southern Medical University, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering of mice.
Mycoplasma Elimination
Aseptic inflammation was induced in BALB/c mice (n = 5) by intraperitoneal injection (i.p) of 0.5 ml sterile paraffin oil (CAS#: 8042-47-5, DAMAO, China) 7 days before the C3A cells injection. 1d M(+) C3A cells were digested with 0.25% trypsin (Gibco, Hangzhou, China, Cat: 25200), centrifuged at 1,200 rpm for 3 min, then resuspended in normal saline at a concentration of 4 × 106 cells /ml. Each mouse was intraperitoneally injected with a 0.5 ml of C3A cell suspension and the mice were sacrificed after 14 days. Ascites were collected using a sterile syringe, and centrifuged at 800 rpm for 5 min to harvest the cells. The cells were resuspended in EMEM medium (20% FBS) to obtain a concentration of 10–20 cells/ml. Cells were plated in 96 well plates (150 μL/well) and incubated for 12 h. The single attached cells in plates were screened by microscopy (Axio Observer, Zeiss). The cells were cultured and degested by 0.25% trypsin when cells showed significant contact inhibition, or were more than 70% confluent, and then reseeded to a larger plate or flask (Figure 1). The process of culture and reseeding continued for 27 days and 5 × 106 cells were harvested for further experiments.
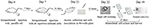
Figure 1. Flowchart of Mycoplasma elimination. Aseptic inflammation was induced in BALB/c mice by intraperitoneal injection (i.p) with 0.5 ml sterile paraffin oil 7 days before cells injection. 1d M(+) cell were intraperitoneal injected with a 0.5 ml of cell suspension (4 × 106/ml) in mice in day 7. Cells from the ascites were collected and inoculated in 96-well plate in day 21. After 12 h, the single attached cells were screened by microscopy and cultured for 27 days. Cells were harvested in 25-cm2 culture flasks in day 49 for further experiments.
Human–Mouse Cell Contamination Testing
Genomic DNA was extracted from Tc, M(−) cell, and control mouse liver AML12 cells (ATCC) using the Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA, Cat: A1120). The integrity of genomic DNA was evaluated electrophoretically. DNA samples were then diluted 1:20 for PCR assays using human and mouse COX-I primers to determine species cross-contaminations (Parodi et al., 2002; Cooper et al., 2007) (primer sequences listed in Table 1). The PCR reaction mixture (25 μl) contained 0.5 μl DNA, 2.5 μl of 2 mM dNTP mixture, 2.5 μl 10 × KOD buffer, 0.3 μL each of forward and reverse primers, 1.5 μL of 25 mM MgSO4, 0.3 μL KOD Plus Neo (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan, Cat: KOD401B), and 17.1 μL ddH2O. The cycling conditions included an initial denaturation step of 94°C for 3 min, followed by 30 cycles of 98°C for 15 s, 58°C for 15 s, and 68°C for 30 s. The final elongation was done at 68°C for 5 min. DNA samples from M(−) cell and AML12 cells were used as positive controls, and ddH2O was used as a negative control. PCR products (5 μL) were analyzed on 1% agarose gels.
Mycoplasma Detection Using Immunofluorescence of Hoechst 33258 DNA Staining
Cells were tested using a Mycoplasma detection kit (C0296, Beyotime, Hangzhou, China) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The assay was based on Hoechst 33,258 staining of Mycoplasma DNA, which was observed and photographed using a fluorescence microscope (Axio Observer, Zeiss).
Detection of XMRV (Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus) by PCR
XMRV was detected by PCR assays as previously described (Naseer et al., 2015). PCR reaction products were identified on 1% agarose gels.
Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR(qRT-PCR) to Determine Levels of Functional Genes in Cells
Total RNA was extracted from Tc, 1d M(+) cell, 43d M(+) cell, and M(−) cell cells using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA, Cat: 15596018) according to the manufacturer's instructions. After reverse transcription, cDNAs were used for qRT-PCR. The reaction mixture (20 μl) contained 5 μl cDNA (1:20 dilution), 0.5 μL each of forward and reverse primers, 10 μl of 2x SYBR Green qRT-PCR SuperMix 10 μl (Invitrogen, Cat:11733038), and 4 μl of RNase-free H2O. Cycling conditions included 1 cycle of 50°C for 2 min, 1 cycle of 95°C for 2 min, and 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s and 60°C for 32 s using an ABI Prism 7500 Sequence Detection System (Application Binary Interface, USA). The primer sequences are listed in Table 1. The mRNA levels were normalized to that of β-actin [ΔCt = ΔCt(gene) − ΔC (β-actin), ΔΔCt = ΔCt (gene in experiment group) − ΔCt (gene in control group) Expression = 2 − ΔΔCt].
Western Blotting to Evaluate Protein Expression
Cell samples were RIPA lysed buffer (P0013E, Beyotime) and protein concentration of the lysates was determined using the BCA kit (P0010S, Beyotime). Protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes, and blocked in 10% milk in Tris-buffered saline. The membranes were then incubated at 4°C overnight in a 1:500 dilution of anti-human ALB (sc-271605, Santa Cruz), and then incubated in HRP-conjugated secondary antibody with a dilution of 1:3,000 for 2 h (BA1051, BA1055, Boster). Protein bands were visualized with an ECL kit (WBKLS0050, Merck Millipore). Data were analyzed using Image J 3.0. The gray ratio of ALB proteins and β-actin represented the relative level of the target protein. CPS1, TF, CYP3A4, CYP2D6 proteins were similarly detected by western blotting using their specific antibodies with the dilutions of 1:500, 1:10,000, 1:2,000, and 1:1,000, respectively (ab64613, ab82411, ab3572 Abcam, 93867s Cell Signaling Technology).
Short Tandem Repeats (STR) Identification of Tc and Data Comparison
STR identification in Tc cells was performed using the PowerPlex16 HS System (Promega Corp, Madison, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions and as previously described (Ensenberger et al., 2010). The technique uses capillary electrophoresis to detect 16 STR loci. The results were compared to the C3A cell information provided by ATCC.
MTT Assay to Detect Cell Proliferation
Cells from the Tc, M(−) cell, 1d M(+) cell, and 43d M(+) cell groups were inoculated in 96-well plates at a density of 1,000 cells/well (200 μl). MTT solution (Invitrogen, Cat: M6494) at a concentration of 5 mg/ml in 0.1 M PBS was added into each well (20 μl/well). All tests were run in at least five wells. The cells were incubated for 4 h at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2 prior to the addition of 150 μl of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) into each well. The cells were incubated for 10 min to dissolve formazan crystals, and the absorbance was read at 490 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-tek Elx800). Five wells containing only medium were used as controls.
Statement of Biohazard Safety
All the procedures followed the guidelines of Biological Safety Regulations of Pathogenic Microbiology Laboratory of China.
Statistical Method
Data are presented by mean ± standard deviation (SD). Differences among groups were assessed using one-way ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric test for continuous variables. Post-hoc pairwise multiple comparisons were made with LSD or Dunnett's procedure if significant differences were found among groups. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Analyses were carried out using SPSS version 22.0.
Results
Detection and Identification of M. hyorhinis
PCR analysis showed the presence of a 343 bp band in all Mycoplasma-infected C3A cells over a duration of 6 days of culture (Figure 2A). DNA sequence analysis of PCR products obtained on days 2, 4, and 6 of culture showed 100% identity with M. hyorhinis DBS 1050. Cell suspensions for intraperitoneal injections contained 6.2 ± 2.2 × 108 CFU/ml of Mycoplasma (Supplementary Figure 1).

Figure 2. Detection of Mycoplasma contamination in infected C3A cells. Lane 1: day 2 culture; lane 2: day 4 culture; lane 3: day 6 culture; lane 4: positive control; lane 5, negative control. (B) Mycoplasma detection in Tc and M(+) cell groups. Lane 1: 1d M(+) cell; lane 2: 8d M(+) cell; lane 3: 15d M(+) cell; lane 4: 22d M(+) cell; lane 5: 27d M(+) cell; lane 6: 36d M(+) cell; lane 7: 43d M(+) cell; lane 8: 1d Tc; lane 9: 8d Tc; lane 10: 15d Tc; lane 11: 22d Tc; lane 12: 29d Tc; lane 13: positive control; lane 14: negative control. (C) Monoclonal human–mice cell contamination. Lane 1: Tc+ human COX-I primers; lane 2: M(−) cell+ human COX-I primers; lane 3: ML12+human COX-I primers; lane 4: ddH20+human COX-I primers; lane 5: Tc+ mice COX-I primers; lane 6: M(−) cell+mice COX-I primers; lane 7: AML12+mice COX-I primers; lane 8: ddH20+mice COX-I primers; lane M, 1-2000-bp DNA marker (Takara).
Monoclonal Cell Selection
Four of five BALB/c mice intraperitoneally injected with 1d M(+) cells exhibited abdominal swelling after 14 days. The cells isolated from ascites of the four mice were separately inoculated in 96 well plates to select monoclonal cells. At 12 h after inoculation, single cell was detected attached to the 96 well plate, and two nuclei, representing the cell in split phase, appeared at 48 h (Figures 3A,B). By day 5, one single cell formed a cell colony with a morphology similar to normal C3A cells (Figure 3C). The single colony continued to grow and multi-layered cells were observed on day 8 which exhibited contact inhibition (Figure 3D). By day 27, the cells exhibited vigorous growth and had formed many colonies (Figure 3E).

Figure 3. Selection and identification of monoclonal cells (Tc). Data are time after inoculation: (A) 12 h, (B) 2 d, (C) 5 d, (D) 8 d, (E) 27 d (25-cm2 tissue flask).
Successful Elimination of M. hyorhinis Confirmed by PCR and TEM
The culture supernatant from Tc and 1d M(+) cell cells was tested for Mycoplasma using PCR assays. The 343 bp band indicating Mycoplasma contamination was seen in cells from the 1d M(+) cell group, and persisted for 43 days. The Tc cells from four mice ascites were shown to be consistently Mycoplasma negative after 27 days of cultivation (Figure 2B).
TEM was used to identify Mycoplasma contamination and the cell state. Cells in the 1d M(+) cell group showed the presence of Mycoplasma around the cytomembrane, the mitochondria showed edema and swelling, intracellular autophagy bodies were detected, and the nuclei appeared swollen with clumped and marginated heterochromatin (Figures 4A1–A4). Most of the 43d M(+) cell cells exhibited the presence of intracellular Mycoplasma, lots of vacuoles, more severe mitochondrion swelling, and swollen nucleus compared to 1d M(+) cell, and apoptotic bodies in the cytoplasm (Figures 4 B1–B4). The presence of cell debris (CD) and nuclear fragments indicated the serious side-effects of Mycoplasma contamination on these cells (Supplementary Figure 2). TEM analysis showed no Mycoplasma either inside or outside of cells from Tc cells treated with intraperitoneal passage in four mice. Tc cells also showed rich microvilli and neatly arranged endoplasmic reticulum, indicating that these cells were not in a condition of apoptosis. Cells from the Tc group had clear Z lines, compact mitochondrial crista and normal intact membrane which significantly differentiated them from the contaminated cell groups (Figures 4C1–C4). At the present time, the resulting cured cells have been cultivated continuously for 18 months, during which regular screening has failed to reveal any mycoplasma infection (data not shown).
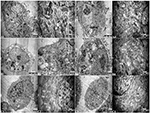
Figure 4. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of (A1–A4), 1d M(+) cell; (B1–B4), 43d M(+) cell; and (C1–C4), Tc. M, Mycoplasma; AB, autophagy body; APB, apoptotic body; Mit, mitochondria; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; V, vacuoles.
Detection of Human–Mouse Cross-Contamination
DNA was extracted from Tc, M(−) cell, and AML12 cells for evaluate human–mouse cell cross-contamination. Human COX-1 primers generated only one band, while the mouse COX-1 primers failed to generate a band when PCR assays were performed on DNA templates from Tc cells. M(−) cells used as a human positive C3A control also showed a single 300-bp band with the human COX-I primers and no band with the mouse COX-1 primers. AML12 cells used as a mouse positive control showed a single 150-bp band with the mouse COX-I primers and no band with human COX-I primers. The negative control group was negative (Figure 2C). These results indicated that there was no contamination of the treated human cells with mouse cells.
STR Identification of Tc
Sixteen STR loci were detected by capillary electrophoresis. Eight STR loci were consistent with C3A data available from ATCC (Figure 5, Table 2). Tc cells were identified as C3A cells without contamination from mice or other species.
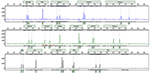
Figure 5. Capillary electrophoresis of Tc (D5S818, TH01, D13S317, D7S820, D16S539, CSF1PO, vWA, TPOX, Amelogenin, D3S1358, D21S11, D18S51, Penta E, Penta D, D8S1179, FGA).
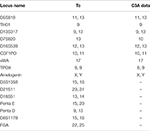
Table 2. Tc STR results and comparison.
Hoechst 33258 Staining and Observation
After Hoechst 33258 staining, Tc showed clear nuclei without any staining around them (Figure 6A). 1d M(+) cells showed the presence of filamentous or small granular blue fluorescence around the nuclei indicating Mycoplasma contamination (White arrow, Figures 6B,C). In 43d M(+) cells, there were very few intact nuclei, and most of the nuclei were broken and fragmented (Figure 6D). Nuclear fragmentation and intense nuclear staining in cells from the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups indicated apoptosis.
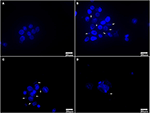
Figure 6. Hoechst 33258 staining (A) Tc, (B,C) 1d M(+) cell, (D) 43d M(+) cell. Mycoplasma (arrow). Tc exhibited distinct nuclei with no evidence of Mycoplasma; 1d M(+) cell exhibited filamentous or small granular blue fluorescence around the nuclei which were evidence of Mycoplasma (White arrow). 43d M(+) cell exhibited broken and fragmented nuclei with almost no intact nuclei observed. Nuclear fragmentation and intense staining was due to DNA condensation during apoptosis1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell cells.
XMRV Detection
PCR assays to detect XMRV in 22Rv1 positive control human prostate cancer cells generated a band of 516 bp. PCR assays on negative control human HepG2 cells and mouse liver AML12 cells were negative (Figure 7). When DNA from Tc samples were used as a template, it was negative for the presence of XMRV.

Figure 7. XMRV PCR detection. Tc cells were negative for XMRV expression. The positive control was 22RV1. The negative controls were AML12 and HepG2 cells. Human and Murine GAPDH gene primers served as the loading controls.
Elimination of Mycoplasma Contamination Partially Restored the Expression of Functional Genes
M(−) cell and Tc groups had almost similar expression levels of albumin (ALB), and this was significantly higher compared to 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.01) (Figure 8A). Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1) expression was highest in the M(−) cell group (P < 0.05), while Tc cells showed higher expression of CPS1 compared to the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.05) (Figure 8B). Transferrin (TF) expression was significantly higher in the M(−) cell and Tc groups compared to the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.01) (Figure 8C). CYP2D6 expression was significantly higher in the M(−) cell group compared to the Tc, 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.01), although Tc cells had a significantly higher expression compared to the 43d M(+) cell group (P < 0.01) (Figure 8D). Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) expression was significantly higher in the M(−) cell and Tc groups compared to the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.01), with the 43d M(+) cell group showing the lowest level (P < 0.05) (Figure 8E).
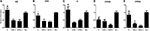
Figure 8. qRT-PCR detection of (A) ALB, (B) CPS1, (C) TF, (D) CYP3A4, (E) CYP2D6. ΔP < 0.05, ΔΔP < 0.01 vs. 1d M(+) cell; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. 43d M(+) cell; ▲P < 0.05, ▲▲P < 0.01, ▲▲▲P < 0.001 vs. M(−) cell.
Elimination of Mycoplasma Contamination Partially Restored the Expression of Functional Proteins
The M(−) cell and Tc groups had almost similar expression levels of ALB protein, and this was significantly higher compared to the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.001) (Figures 9A,B). CPS1 protein levels were highest in the M(−) cell group (P < 0.01), and the Tc group had significantly higher CPS1 protein expression compared to the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.001). The 1d M(+) cell group showed a significantly higher CPS1 protein expression compared to the 43d M(+) cell group (P < 0.05) (Figure 9C). TF protein expression was significantly higher in the M(−) cell and Tc groups compared to the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.05, P < 0.001) (Figure 9D). CYP2D6 expression was significantly higher in the M(−) cell group compared to the Tc, M(+) cell, and 43dM(+) cell groups (P < 0.01), with the Tc group having significantly higher CYP2D6 levels than the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.01) (Figure 9E). The M(−) cell and Tc groups had significantly higher expression of CYP3A4 protein than the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001), with the 43d M(+) cell group showing the lowest expression (P < 0.001) (Figure 9F).
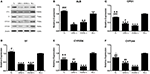
Figure 9. Western-Blot detection of (A) protein bands (B) ALB, (C) CPS1, (D) TF, (E) CYP3A4, (F) CYP2D6. ΔP < 0.05, ΔΔP < 0.01, ΔΔΔP < 0.001 vs. 1d M(+) cell; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. 43d M(+) cell; ▲P < 0.05, ▲▲P < 0.01, ▲▲▲P < 0.001 vs. M(−) cell.
MTT Assay of Cell Proliferation
There was no significant difference in proliferation between the Tc and M(−) cell groups except on day 5 (P < 0.05). Both groups had a significantly higher proliferation rate compared to the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups (Figure 10).
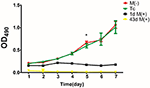
Figure 10. Cell proliferation evaluated by MTT assay. *P < 0.001 compared with 1dM(+) cell.
Discussion
In this study, we describe a technique to eliminate M. hyorhinis contamination in C3A human hepatocyte cells by intraperitoneal passage of contaminated cells in BALB/c mice. Using PCR assays with human- and mouse-specific COX-I and XMRV primers, we showed that there was no XMRV infection or cross-contamination between human and mouse cells. The decontamination was successful and lasted for more than 4 weeks without re-infection. Furthermore, the decontamination process did not compromise cell proliferation and restored the expression of important functional genes and proteins which were down-regulated in contaminated cells.
Although Mycoplasma infection is an insidious problem in mammalian cell culture (Gedye et al., 2015), it can be eliminated by in vitro and in vivo management. It was previously reported than an efficient way to eliminate Mycoplasma contamination involved intraperitoneal injection of BALB/c mice with pristanee in order to induce an inflammatory reaction and formation of ascites within 20–54 days after intraperitoneal injection with contaminated cells (Schimmelpfeng et al., 1980; Howell et al., 1982; Lombardo and Lanks, 1982; Roseto et al., 1984; Carroll and O'Kennedy, 1988; Hirschberg et al., 1989). Injection of Mycoplasma-contaminated cells into the abdomen of these mice resulted in elimination of Mycoplasma, and this was thought to be due to the activity of macrophages and cytokines released in the ascites (Roseto et al., 1984; Hirschberg et al., 1989). This was the same mechanism underlying a second previously described technique which involved the intraperitoneal injection of contaminated cell lines in nude mice without mineral oil; cells were collected by sequential washings with a syringe (Howell et al., 1982). Although the in vivo passage method has been validated previously, it needs a long duration (20–54 days) to form the ascitic fluid in infected mice (Schimmelpfeng et al., 1980; Howell et al., 1982; Lombardo and Lanks, 1982; Roseto et al., 1984; Carroll and O'Kennedy, 1988; Hirschberg et al., 1989). In the present study, we aimed to shorten the process of Mycoplasma decontamination by injecting normal BALB/c mice with paraffin oil injection prior to injecting them with Mycoplasma-infected cells.
A previous study (Lombardo and Lanks, 1982) reported that mycoplasma-free cultures could be obtained from ascites after 27 days in vivo but not after 14 days, without using paraffin oil or pristane prior to injection of cells. Using pristane as a stimulator of inflammation, Hirschberg and et al. proved that 20 days in vivo passage was enough for ascites collection, but a shorter time for in vivo passage of cells was not tested in their study (Hirschberg et al., 1989). In this study, we sought to shorten the time for in vivo passage by injecting the mice with paraffin oil before intraperitoneal injection with cells. Based on previous studies (Lombardo and Lanks, 1982), we considered that 14 days for in vivo passage was the time-frame we might challenge in this study.
We used paraffin oil instead of pristane to induce sterile inflammation prior to injection with 0.5 ml cells suspension (4.0 × 106/ml cells) contaminated with 6.2 ± 2.2 × 108 CFU/ml of M. hyorhinis. Abdominal swelling was observed, and ascites were collected 14 days in four of five mice after intraperitoneal injection with cells. The monoclonal cells from ascites were expanded, and were Mycoplasma-free after continuous regular detections over a period of 18 months. Successful elimination of Mycoplasma from C3A cells was achieved by intraperitoneal passage in four of five mice. The duration of in vivo passage in this study was shortened to 14 days, which was a significant time-saving advantage compared to previous similar studies.
In most previous studies, in vivo passage was used to treat human–murine hybridoma or murine cell lines, which made it difficult to determine cross-contamination between murine and human cells. In our present study, we investigated whether contamination of BALB/c mouse cells could be avoided during in-vivo passage by using a human hepatocyte cell line, C3A, for elimination testing. Since infected cells themselves are the single most important source of further contamination (Hirschberg et al., 1989), all cells were placed in separate environments with the same culture parameters. We initially used PCR and DNA sequencing to examine Mycoplasma contamination from C3A cells and identify the species of Mycoplasma. Our data showed that all three samples (days 2, 4, 6) were contaminated with M. hyorhinis. It has long been assumed that Mycoplasmas exist outside of the eukaryotic cell membrane and the pathogenesis is mediated via cytoadherence. However, Mycoplasma fermentans, Mycoplasma suis, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae have been identified intracellularly, and it is thought that the intracellular location, even for a short period, could sequester and protect Mycoplasma from the effect of antibiotics (Drexler and Uphoff, 2002; Felder et al., 2011; Falagan-Lotsch et al., 2015). Our TEM and immunostaining results confirmed that M. hyorhinis was able to grow intracellularly as well as extracellularly. These data were consistent with a previous study (Mosmann et al., 1986, 2005), and suggested that contamination with M. hyorhinis could result in a high risk of treatment failure with antibiotic therapy. Our present data showed that after intraperitoneal injection of BALB/c mice with contaminated cells, and from the time of seeding the monoclonal cells in plates, the culture supernatants were negative for Mycoplasma for a duration of 4 weeks. PCR, TEM, and Hoechst 33258 staining of Tc showed no evidence of Mycoplasma contamination either intracellularly or extracellularly, suggesting that our method was effective.
Although it has been shown that phagocytosis by macrophage-mediated phagocytosis could play a role in the elimination of extracellular Mycoplasma (Schimmelpfeng et al., 1980), the precise mechanisms underlying the elimination of intracellular Mycoplasma remain unclear. It has been suggested that Mycoplasma-infected cells could be lysed in the presence of MTM (microbial T cell mitogens) by MTM-stimulated CD8+ lymphocytes as well as by MHC class I-restricted CTL clones of defined antigen specificity (Herrmann et al., 1990). This would result in the release of intracellular Mycoplasma from the lysed cells, which would be susceptible to phagocytosis (Hickmandavis et al., 2001; Woolard et al., 2005). Release of cytokines such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin-2 (IL-2), tumor necrosis factor beta (TNF-β also known as lymphotoxin), granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and granulysin by Th1 cells and CD8+ T cells has been shown to amplify the host immune response to intracellular microbes, and enhancing cellular immunity (Mosmann et al., 1986, 2005; Mosmann and Coffman, 1989; Stenger et al., 1998; Heidegger et al., 2015; Kornspan et al., 2015). It will be interesting to further understand the mechanisms underlying Mycoplasma decontamination in our experimental system.
Due to concerns about human–mouse cross-contamination, we selected monoclonal cells and determined COX-I expression, which is an easy and effective way to determine contamination of cells across different species (Hebert et al., 2003; Cooper et al., 2007; Ensenberger et al., 2010). Based on our PCR results using COX-I primers, we excluded the possibility of human murine cell cross-contamination, which were further confirmed by STR detection. Our data suggested that this technique was successful in preventing murine cell contamination of treated cells.
Human cells grown as xenografts in mice have a risk of being infected with murine retroviruses, of which XMRV is a potential human pathogen (Paprotka and Pathak, 2011; Delviksfrankenberry et al., 2012; Naseer et al., 2015). Our PCR results using XMRV primers showed no evidence of XMRV infection.
M. hyorhinis is one of the most common species of infectious Mycoplasma and represents 10–40% of the Mycoplasma contamination in a cell culture (UKCCCR, 2000; Drexler and Uphoff, 2002; Zinöcker et al., 2011; Vande et al., 2014; Olareringeorge and Hogenesch, 2015). M. hyorhinis infection has been shown to degrade host cell DNA, induce malignant transformation of human prostate cells, inhibit lymphocyte proliferation, and decrease the cytostatic activity of chemotherapy drugs (Paddenberg et al., 1998; Namiki et al., 2009; Zinöcker et al., 2011; Vande et al., 2014). However, it is not clear whether M. hyorhinis could lead to irreversible changes in C3A cells, or whether in vivo Mycoplasma elimination could reverse the expression of functional genes in these cells. We compared the mRNA and protein levels of important functional genes including those involved in protein synthesis (ALB, TF), ammonia metabolism (CPS1), and drug metabolism (CYP2D6, CYP3A4) (Rothschild et al., 1988; Beutler et al., 2000; Zhou et al., 2009; Wright et al., 2011), in all the cell groups. Compared to the Tc and M(−) cell groups, the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups showed a significant decrease in the expression of ALB, CPS1, TF, CYP3A4, and CYP2D6 genes as well as proteins. There was no significant difference in the gene or protein levels of ALB, or TF between the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups. The expression levels of CPS1, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 proteins were significantly lower in the 43d M(+) cell group compared to the 1d M(+) cell group, suggesting that the extent of CPS1, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 inhibition was related to the length of infection. Additionally, since these proteins play important roles in various metabolic pathways, it is possible that there could be a further time-dependent decrease in the metabolism of Mycoplasma-infected cells. Elimination of Mycoplasma infection restored the levels of ALB, TF, and CYP3A4 genes as well as proteins to normal levels. However, the levels of CPS1 and CYP2D6 genes and proteins did not return to the levels observed in M(−) cell. These data were consistent with previous reports that showed that Mycoplasma infection resulted in irreversible, permanent changes in the expression of P53, RB and a number of other genes (Paddenberg et al., 1998; Zhang et al., 2006; Namiki et al., 2009; Zinöcker et al., 2011; Vande et al., 2014). Interestingly, although the expression of CPS1 and CYP2D6 in the Tc group did not reach that of the M(−) cell group, both genes and proteins were significantly up-regulated compared with the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups. These data suggested that our technique did improve cell function.
MTT assays showed no significant difference in cell proliferation between the Tc and M(−) cell groups, which had higher rates of proliferation than the 1d M(+) cell and 43d M(+) cell groups. Our TEM data revealed rich microvilli, neatly arranged endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria with compact crista, intact membrane, and clear Z lines in the Tc group. These data were evidence of strong metabolism and protein synthesis activity in cells from the Tc group.
Compared to antibiotic treatment, our method needs more technical skills in animal handling, which is one of the limitations of this study. Another limitation was that we only tested one concentration of cells and Mycoplasma. The threshold of Mycoplasma contamination which could be removed through this system should be further examined. In addition, the functions of some genes were not 100% recovered after the treatment, and whether it was related with the irreversible cellular damage caused by Mycoplasma infection remained unknown. Further study is needed to investigate the reasons why some genes function could not completely recover to normal level using this method.
In summary, we describe a reliable method to eliminate Mycoplasma both inside and outside of culture cells without inducing cell-cross contamination or XRMV infection. Compared to the previous similar studies, the duration of intraperitoneal passage in this study was significantly shorter. This decontamination technique significantly improved the function and proliferation of treated cells, and may be used as an alternative to antibiotic treatment for Mycoplasma contamination in important or irreplaceable cell lines.
Author Contributions
JW and YL mainly completed this study, who contributed equally to this work. JW finished the first draft. LC gave help in the animal test. TL assisted the cell experiment. GP and CF offered help in the WB experiment. XH offered help in MTT. HL offered help in QPCR. ZJ, ZZ, and JD offered help in other experiment. QP and YG designed the experiment, provided funding and revised the paper.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer YB and handling Editor declared their shared affiliation.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81470875), (81600489) the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2014A030312013), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (2015B090903069), (2014B020227002), (2013B091100001), (2015B020229002), and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou, China (201604020002).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00440/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1. Mycoplasma culture number counting, (A) 40×; (B) 100×; (C) 200×. M. hyorhinis concentration was 6.2 ± 2.2 × 108CFU/ml.
Supplementary Figure S2. (A–D) TEM of 43d M(+) cell. M, Mycoplasma; CD, Cell debris; N, Nuclear Fragments.
References
Beutler, E., Gelbart, T., Lee, P., Trevino, R., Fernandez, M. A., and Fairbanks, V. F. (2000). Molecular characterization of a case of atransferrinemia. Blood 96, 4071–4074.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Carroll, K., and O'Kennedy, R. (1988). The elimination of mycoplasma from infected hybridomas by passaging in BALB/c mice. J. Immunol. Methods 108, 189–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90418-8
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cooper, J. K., Sykes, G., King, S., Cottrill, K., Ivanova, N. V., Hanner, R., et al. (2007). Species identification in cell culture: a two-pronged molecular approach. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 43, 344–351. doi: 10.1007/s11626-007-9060-2
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Degeling, M. H., Maguire, C. A., Bovenberg, M. S., and Tannous, B. A. (2012). Sensitive assay for mycoplasma detection in mammalian cell culture. Anal. Chem. 84, 4227–4232. doi: 10.1021/ac2033112
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Delviksfrankenberry, K., Cingoz, O., Coffin, J. M., and Pathak, V. K. (2012). Recombinant origin, contamination, and de-discovery of XMRV. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2, 499–507. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.06.009
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Drexler, H. G., and Uphoff, C. C. (2002). Mycoplasma contamination of cell cultures: incidence, sources, effects, detection, elimination, prevention. Cytotechnology 39, 75–90. doi: 10.1023/A:1022913015916
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ensenberger, M. G., Thompson, J., Hill, B., Homick, K., Kearney, V., Mayntz-Press, K. A., et al. (2010). Developmental validation of the PowerPlex 16 HS System: an improved 16-locus fluorescent STR multiplex. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 4, 257–264. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2009.10.007
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Falagan-Lotsch, P., Lopes, T. S., Ferreira, N., Balthazar, N., Monteiro, A. M., Borojevic, R., et al. (2015). Performance of PCR-based and bioluminescent assays for mycoplasma detection. J. Microbiol. Methods 118, 31–36. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2015.08.010
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Felder, K. M., Hoelzle, K., Ritzmann, M., Kilchling, T., Schiele, D., Heinritzi, K., et al. (2011). Hemotrophic mycoplasmas induce programmed cell death in red blood cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 27, 557–564. doi: 10.1159/000329957
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Gedye, C., Cardwell, T., Dimopoulos, N., Tan, B. S., Jackson, H., Svobodová, S., et al. (2015). Mycoplasma infection alters cancer stem cell properties in vitro. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 12, 1–6. doi: 10.1007/s12015-015-9630-8
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Hebert, P. D., Ratnasingham, S., and Dewaard, J. R. (2003). Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. Biol. Sci. 270 (Suppl. 1), S96–S99. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2003.0025
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Heidegger, S., Jarosch, A., Schmickl, M., Endres, S., Bourquin, C., and Hotz, C. (2015). Mycoplasma hyorhinis-contaminated cell lines activate primary innate immune cells via a protease-sensitive factor. PLoS ONE 10:e0142523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142523
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Herrmann, T., Maryanski, J. L., Romero, P., Fleischer, B., and Macdonald, H. R. (1990). Activation of MHC class I-restricted CD8+ CTL by microbial T cell mitogens. Dependence upon MHC class II expression of the target cells and V beta usage of the responder T cells. J. Immunol. 144, 1181–1186.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Hickmandavis, J. M., Fang, F. C., Nathan, C., Shepherd, V. L., Voelker, D. R., and Wright, J. R. (2001). Lung surfactant and reactive oxygen-nitrogen species: antimicrobial activity and host-pathogen interactions. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 281, 517–523.
Google Scholar
Hirschberg, L., Bölske, G., and Holme, T. (1989). Elimination of mycoplasmas from mouse myeloma cells by intraperitoneal passage in mice and by antibiotic treatment. Hybridoma 8, 249–257. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.249
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Hopfe, M., Deenen, R., Degrandi, D., Köhrer, K., and Henrich, B. (2013). Host cell responses to persistent mycoplasmas–different stages in infection of HeLa cells with Mycoplasma hominis. PLoS ONE 8:e54219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054219
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Howell, D. N., Machamer, C. E., and Cresswell, P. (1982). Elimination of mycoplasma from human B-lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum. Immunol. 5, 233–238. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90136-7
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Kazemiha, V. M., Bonakdar, S., Amanzadeh, A., Azari, S., Memarnejadian, A., Shahbazi, S., et al. (2016). Real-time PCR assay is superior to other methods for the detection of mycoplasma contamination in the cell lines of the National Cell Bank of Iran. Cytotechnology 68, 1063–1080. doi: 10.1007/s10616-015-9862-0
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Kornspan, J. D., Tsur, M., Tarshis, M., Rottem, S., and Brenner, T. (2015). Mycoplasma hyorhinis induces proinflammatory responses in mice lymphocytes. J. Basic Microbiol. 55, 679–684. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201400287
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Laleh Nikfarjam, P. F. (2012). Prevention and detection of mycoplasma contamination in cellculture. Cell J. 13, 203–212.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Lincoln, C. K., and Gabridge, M. G. (1998). Chapter 4 cell culture contamination: sources, consequences, prevention, and elimination. Methods Cell Biol. 57, 49–65. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(08)61571-X
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Lombardo, J. M., and Lanks, K. W. (1982). Elimination of M. hyorhinis from murine neuroblastoma cell lines by in vivo passage. In Vitro 18(3 Pt. 1), 251–253.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Mosmann, T. R., Cherwinski, H., Bond, M. W., Giedlin, M. A., and Coffman, R. L. (1986). Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J. Immunol. 136, 2348–2357.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Mosmann, T. R., Cherwinski, H., Bond, M. W., Giedlin, M. A., and Coffman, R. L. (2005). Pillars article: two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. 1986. J. Immunol. 175, 5–14.
Mosmann, T. R., and Coffman, R. L. (1989). TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Immunology 7, 145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Namiki, K., Goodison, S., Porvasnik, S., Allan, R. W., Iczkowski, K. A., Urbanek, C., et al. (2009). Persistent exposure to Mycoplasma induces malignant transformation of human prostate cells. PLoS ONE 4:e6872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006872
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Naseer, A., Terry, A., Gilroy, K., Kilbey, A., Watts, C., Mackay, N., et al. (2015). Frequent infection of human cancer xenografts with murine endogenous retroviruses in vivo. Viruses 7, 2014–2029. doi: 10.3390/v7042014
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Olareringeorge, A. O., and Hogenesch, J. B. (2015). Assessing the prevalence of mycoplasma contamination in cell culture via a survey of NCBI's RNA-seq archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 2535–2542. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv136
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Paddenberg, R., Weber, A., Wulf, S., and Mannherz, H. G. (1998). Mycoplasma nucleases able to induce internucleosomal DNA degradation in cultured cells possess many characteristics of eukaryotic apoptotic nucleases. Cell Death Differ. 5, 517–528. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400380
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Parodi, B., Aresu, O., Bini, D., Lorenzini, R., Schena, F., Visconti, P., et al. (2002). Species identification and confirmation of human and animal cell lines: a PCR-based method. Biotechniques 32, 432–434, 436, 438–440.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Roseto, A., Guillemin, M. C., Chehimi, J., Mazeron, M. C., and Périès, J. (1984). Elimination of mycoplasma, bacteria, and fungi contaminants of hybridoma cultures by intraperitoneal passage in the mouse. Hybridoma 3, 297–300. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1984.3.297
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Stenger, S., Hanson, D. A., Teitelbaum, R., Dewan, P., Niazi, K. R., Froelich, C. J., et al. (1998). An antimicrobial activity of cytolytic T cells mediated by granulysin. Science 282, 121–125.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
UKCCCR (2000). UKCCCR guidelines for the use of cell lines in cancer research. Br. J. Cancer 82, 1495–1509. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.1999.1169
CrossRef Full Text
Vande, V. J., Sabuncuoglu, S., Noppen, S., Hofer, A., Ranjbarian, F., Fieuws, S., et al. (2014). Nucleoside-catabolizing enzymes in mycoplasma-infected tumor cell cultures compromise the cytostatic activity of the anticancer drug gemcitabine. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 13054–13065. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.558924
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Woolard, M. D., Hudig, D., Tabor, L., Ivey, J. A., and Simecka, J. W. (2005). NK cells in gamma-interferon-deficient mice suppress lung innate immunity against Mycoplasma spp. Infect. Immun. 73, 6742–6751. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6742-6751.2005
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Wright, G., Noiret, L., Olde Damink, S. W., and Jalan, R. (2011). Interorgan ammonia metabolism in liver failure: the basis of current and future therapies. Liver Int. 31, 163–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02302.x
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Zhang, S., Tsai, S., and Lo, S. C. (2006). Alteration of gene expression profiles during mycoplasma-induced malignant cell transformation. BMC Cancer 6:116. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-116
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Zinöcker, S., Wang, M. Y., Gaustad, P., Kvalheim, G., Rolstad, B., and Vaage, J. T. (2011). Mycoplasma contamination revisited: mesenchymal stromal cells harboring mycoplasma hyorhinis potently inhibit lymphocyte proliferation in vitro. PLoS ONE 6:e16005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016005
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
How to Get Rid of Mycoplasma in Cell Culture
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/269196